STAF Ballscrews

Ball Screw Model Number Coding

Shaft Model Number Coding
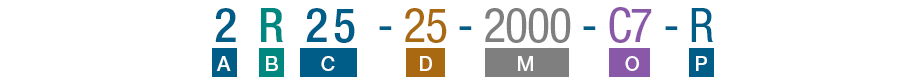
Nut Model Number Coding

- A
- Number of Thread
- B
- Thread direction
- R:Right hand
- L:Left hand
- C
- Nominal diameter
(Size)
- D
- Lead
- E
- Number of turns
- T:0.5~1
- A:1.5~2
- B:2.5~3
- C:3.54
- D:4.5~5
- F
- Number of nut Circuits
- G
- Number of Nut
- H
- Mounting:
- F:Flanged
- R:Non-Flanged
- X:Special Flange
- I
- Nut type
- S:Single nut
- D:Double nut
- J
- Circulation type
- I:Internal
- E:High Lead
- C:Low voice
- U:DIN69051
- Y:None flange
- K:Miniature
- K
- Flange type
- N:Non-cutting
- S:Single-cutting
- D:Double-cutting
- A:Round ball nut
- L
- Circulator type
- I:Iron Circulator
- P:Plastic Circulator
- M
- Tread length (mm)
- N
- Total Shaft length
- O
- Accuracy
- C3:0.008
- C5:0.018
- C7:0.05
- C10:0.21
- P
- R:Rolled ball screw
- G:Ground ball screw
- Q
- Axial clearance & preload code
- P0:With backlash
- P1:Non-backlash
- P2:Light preload
- P3:Heavy preload
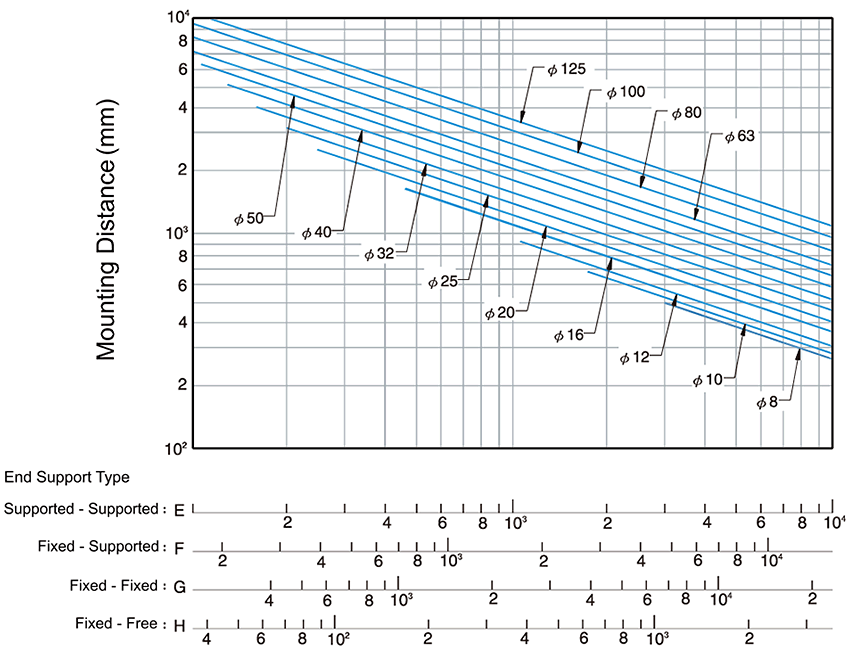
Permissible Axial Load
Ballscrew to be used should not buckle under the maximum compressive load applied in its axial direction.
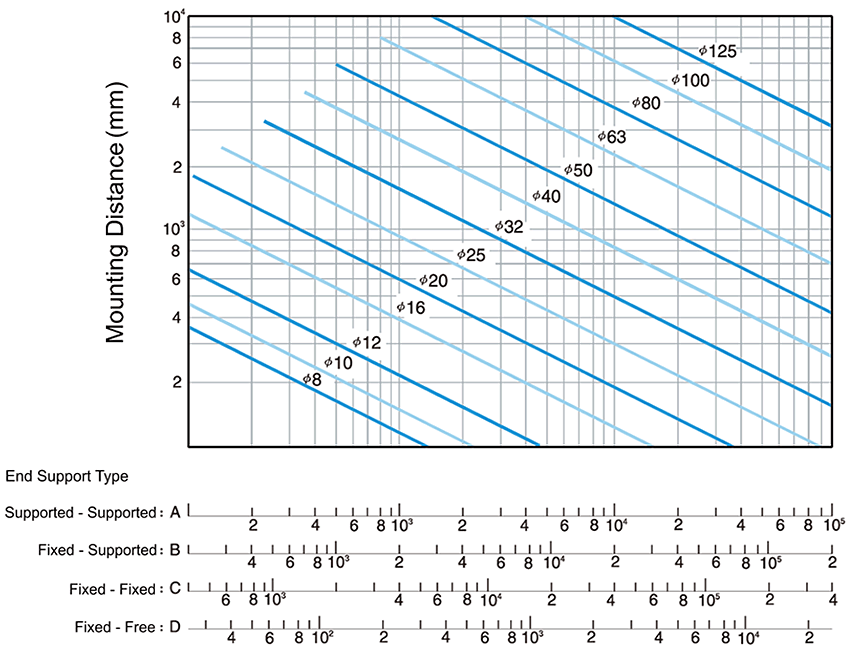
Permissible Rotational Speed
When the rotation speed of driving motor coincides with the natural frequency of feed system (mainly the ballscrew), the resonance of vibration shall be triggered. This rotation speed is then called critical rotation speed. It shall make bad quality machining, since there is wave shape surface on the workpiece. It may also cause damage of machine. Hence it is very important to prevent the resonance of vibration from happening. We choose 80% of critical rotation speed as allowable speed.